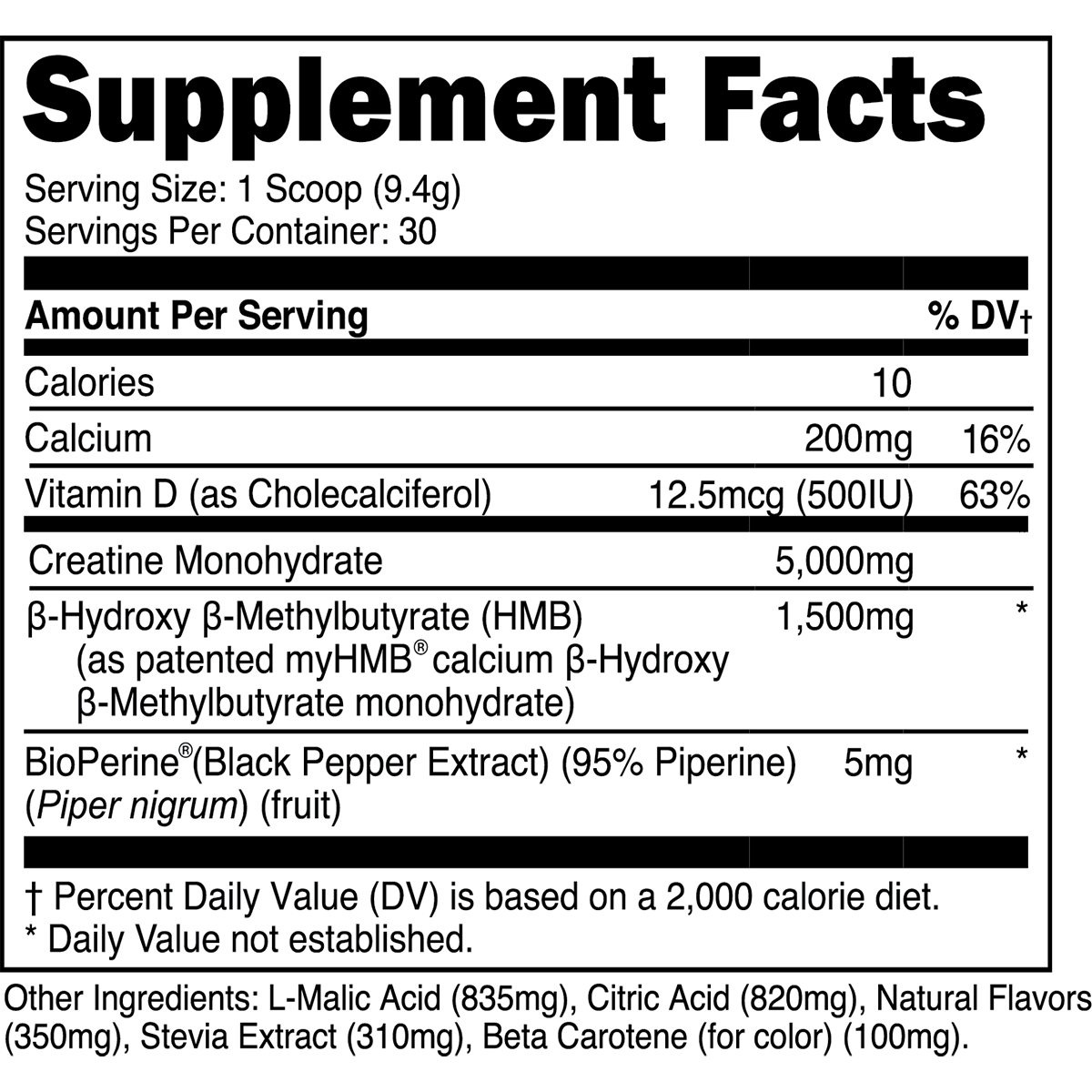
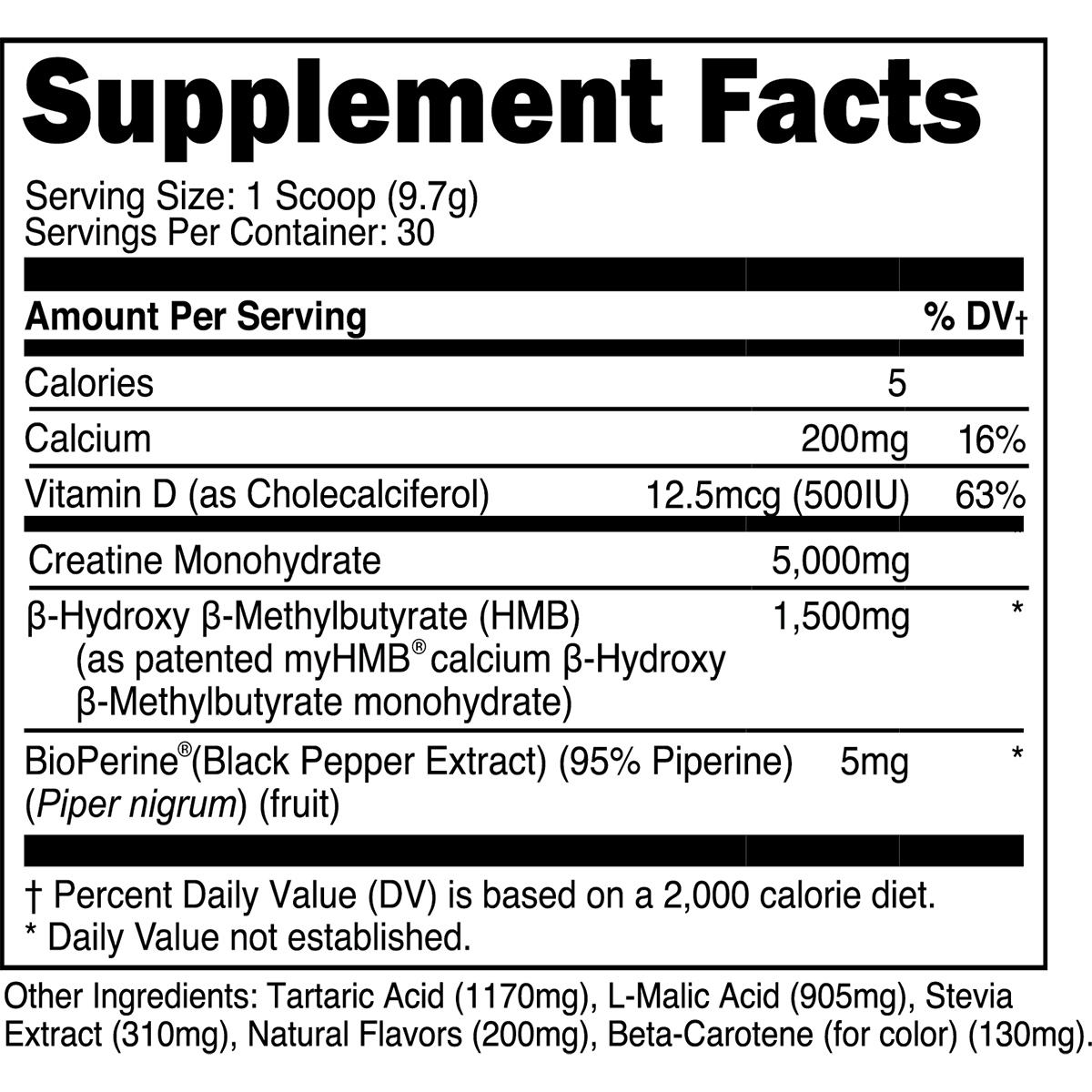
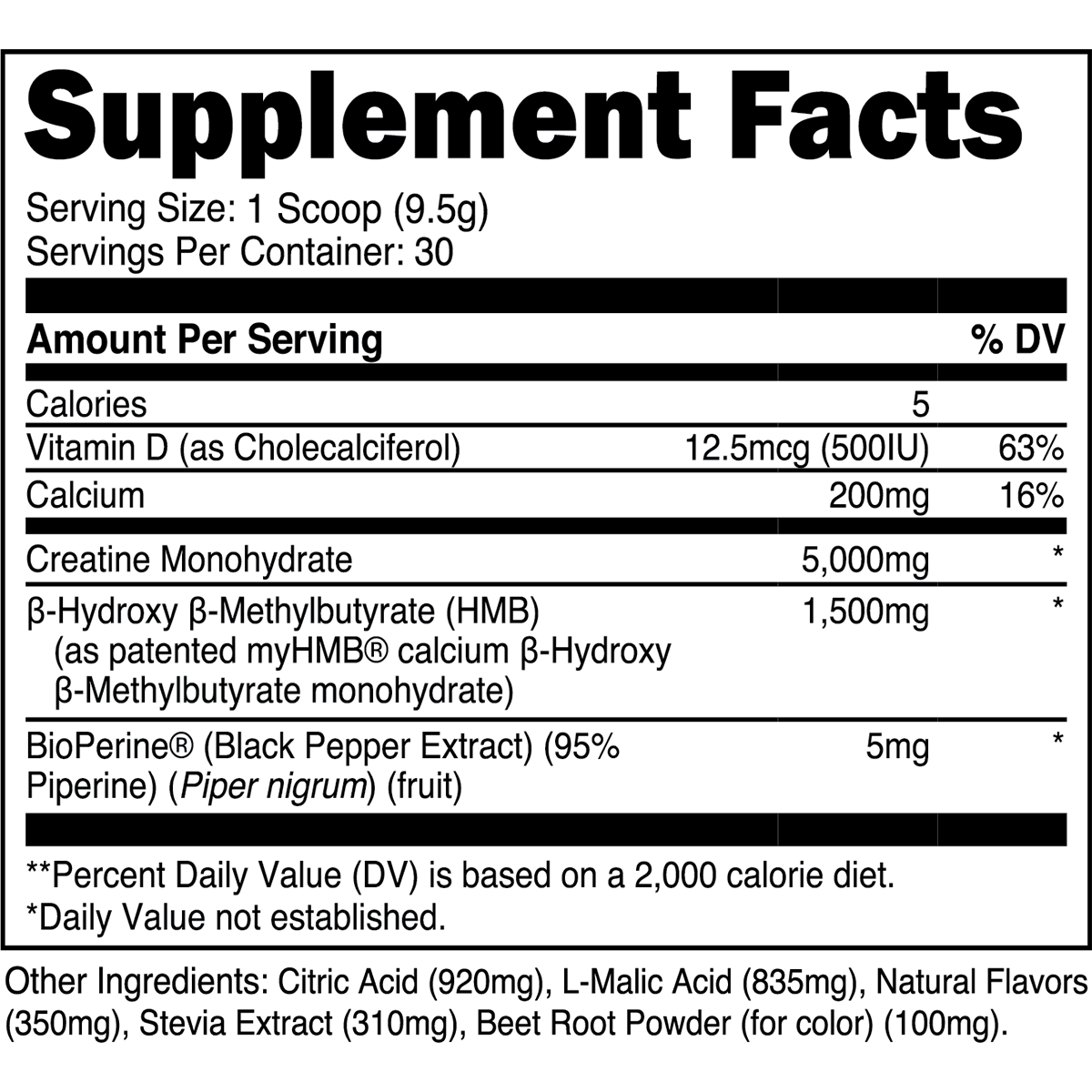
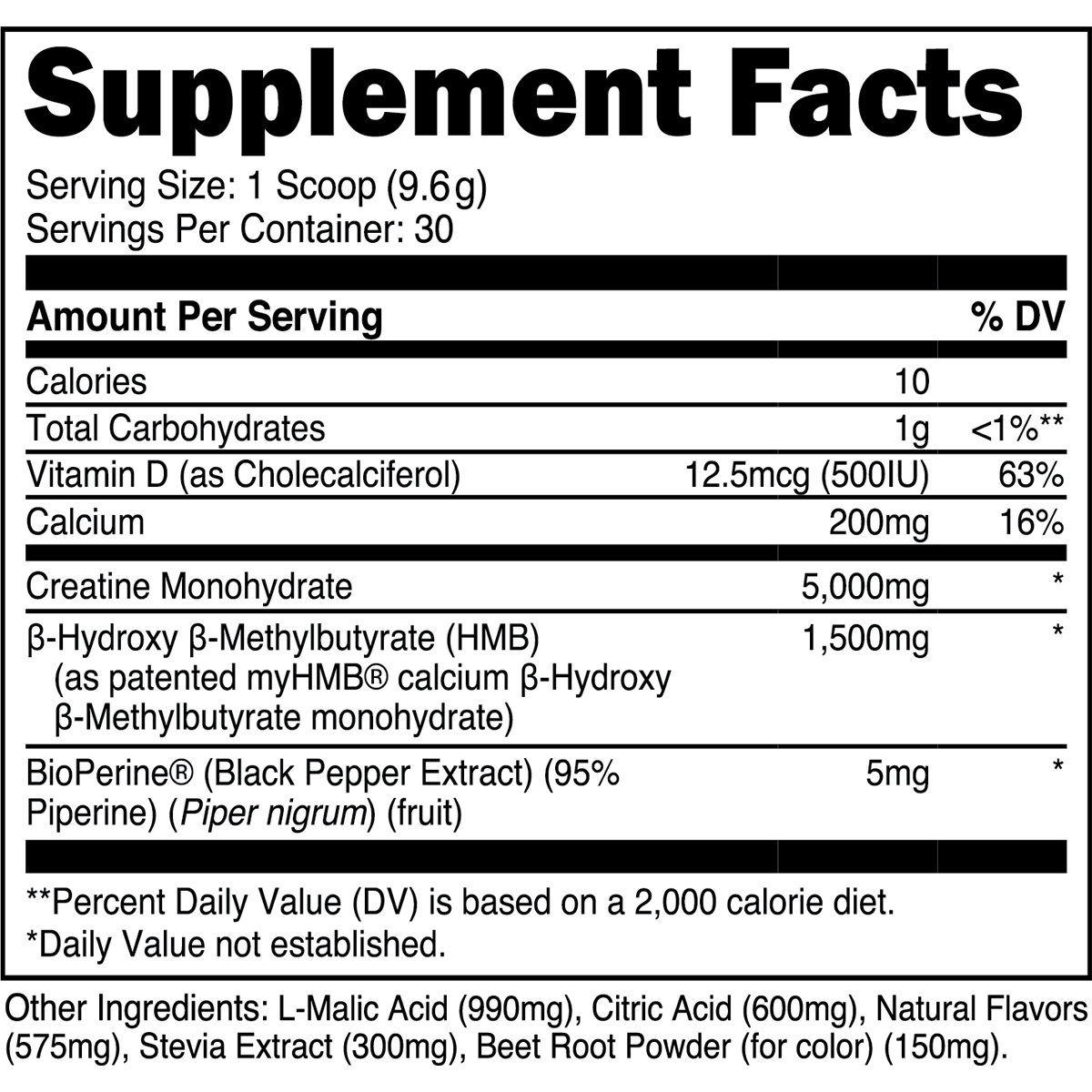
Does cardio build muscle? Yes, certain types do. This article explores effective cardio methods for muscle gain, how to blend cardio with resistance training, and tips to maximize your results.
Cardio doesn’t build muscle like weight training, but it also won’t cause muscle loss when balanced properly. In fact, adding cardio to a well-rounded routine can help you reach your fitness goals more effectively. If you're focused on strength training, don't cut out cardio completely—it still plays an important role in overall progress.
Key Takeaways
-
Cardio can help build muscle when combined with resistance training, but balance is key to avoid muscle breakdown.
-
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is particularly effective for muscle growth and endurance, while Low-Intensity Steady-State (LISS) is better for recovery and maintaining fitness.
-
Nutrition and recovery are essential for maximizing muscle gains; prioritize protein intake post-workout and ensure adequate hydration.
The Science Behind Cardio and Muscle Growth
Cardio exercise is often synonymous with burning calories and improving cardiovascular health, but did you know it can also aid in muscle growth? Yes, cardio builds muscle, especially when effectively combined with resistance training. This synergy is where the magic happens, as incorporating cardio into your workout routine can enhance blood flow, delivering more oxygen and nutrients to your muscle tissue, thus aiding muscle protein synthesis and overall muscle gain.
However, not all cardio workouts are created equal. High-intensity cardio exercises, like HIIT, can contribute to muscle hypertrophy by promoting lean body mass and increasing muscle size. On the flip side, too much cardio can lead to muscle protein breakdown, particularly if not balanced with adequate strength training and recovery. This is a fine line to tread, as increased cardio may also elevate stress hormones like cortisol, which can negatively affect muscle growth.

Understanding these dynamics is crucial for anyone looking to build muscle while maintaining cardiovascular health. Strategically combining cardio and strength training creates a balanced and effective workout routine, enhancing muscle hypertrophy and overall fitness.
How Different Types of Cardio Affect Muscle Mass
Different types of cardio exercises impact muscle mass in various ways. While some forms, like HIIT and HIIRT, are known for promoting muscle growth, others, like LISS, have a different set of benefits.
Explore how these cardio workouts can be optimized for muscle gain.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) stands out for its dual benefits of boosting cardiovascular fitness and promoting muscle hypertrophy. HIIT involves short bursts of intense activity followed by rest or low-intensity periods. This structure not only improves aerobic capacity but also engages muscle fibers in a way that traditional cardio exercises might not.
A 2018 study showed that participants in a HIIT program experienced significant increases in lean body mass and muscle strength. This is because HIIT enhances both aerobic and anaerobic systems, making it possible to gain muscle while improving endurance and burning calories efficiently.
Common HIIT workouts include sprinting, cycling sprints, and bodyweight exercises like burpees and jump squats. These exercises not only help in burning calories but also in building explosive strength, making HIIT a comprehensive workout for muscle building and cardiovascular health.

Low-Intensity Steady-State (LISS)
Low-Intensity Steady-State (LISS) cardio involves performing activities at a constant, moderate pace for an extended period. While LISS is excellent for improving overall fitness and endurance, its direct impact on muscle hypertrophy is limited. This type of cardio primarily engages the aerobic energy system, which is less effective for stimulating significant muscle growth compared to more intense forms of exercise.
However, LISS can complement a weight training program by enhancing recovery and helping to maintain a healthy weight, which indirectly supports muscle growth. Activities such as brisk walking, light jogging, or steady cycling are common examples of LISS that can be incorporated into your routine for overall cardiovascular benefits without significant muscle loss.
Hybrid Interval Resistance Training (HIIRT)
Hybrid Interval Resistance Training (HIIRT) combines the benefits of cardio and resistance training into one effective workout. This approach involves alternating between high-intensity cardio exercises and resistance training exercises, leading to both muscle strength gains and improved cardiovascular health.
HIIRT workouts might include circuits combining weight lifting with short bursts of cardio, such as jumping rope or treadmill sprints. This blend not only maximizes calorie burn but also targets muscle fibers in a way that promotes muscle hypertrophy and endurance simultaneously.
Incorporating HIIRT into your training program effectively enhances muscle building and cardiovascular fitness.
Concurrent Training: Combining Cardio and Weight Training
Combining cardio and weight training, known as concurrent training, can yield impressive results for body composition and overall health. When done correctly, this approach can enhance muscle growth and cardiovascular health simultaneously. However, it is essential to recognize and manage the potential interference effect, which can occur when endurance and resistance training are not properly balanced.
Avoid compromising strength gains by separating cardio and resistance training sessions or strategically sequencing them to minimize negative interactions. For instance, performing weight training before cardio can help prioritize muscle hypertrophy, while doing cardio separately can still provide its cardiovascular benefits without hindering muscle gains.
Recovery is another crucial aspect of concurrent training. Adequate rest, nutrition, and hydration are essential to optimize the benefits of combining cardio and weight training. Carefully planning your workout routine and incorporating recovery strategies ensures a balanced approach supporting both muscle growth and cardiovascular health.
The Role of Mitochondria in Muscle Building
Mitochondria, the powerhouses of our cells, play a pivotal role in muscle building. Their primary function is to convert nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of the cell, which is essential for muscle contractions during exercise. Enhanced mitochondrial function is a key factor in improving exercise efficiency and supporting muscle hypertrophy.
Endurance training, such as aerobic exercise, stimulates mitochondrial biogenesis—the process of forming new mitochondria. This increase in mitochondrial density in muscle cells enhances the muscle’s ability to utilize oxygen and produce ATP, thereby improving endurance and overall performance. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is also known to boost mitochondrial respiration, further supporting muscle growth and recovery.
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARγ) coactivator family is a significant regulator of mitochondrial biogenesis and muscle hypertrophy. Understanding and leveraging the role of mitochondria in muscle building enhances training outcomes and promotes significant muscle gains.
Anaerobic vs Aerobic Respiration: Implications for Exercise
The energy systems your body uses during exercise can significantly impact your performance and muscle growth. Anaerobic and aerobic respiration are the two primary processes that fuel your workouts.
Understanding how each works can help you tailor your training for optimal results.
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration occurs during high-intensity exercises where the body generates energy without oxygen, primarily using glucose stored in muscle glycogen. This process produces ATP quickly but is only sustainable for short bursts of activity due to the accumulation of lactic acid, which can inhibit further ATP production and contribute to muscle fatigue.
Activities such as sprinting, heavy weight lifting, and HIIT rely heavily on anaerobic respiration. These high-intensity efforts are crucial for building explosive strength and muscle hypertrophy but require adequate recovery to manage lactic acid buildup and prevent overtraining.
Aerobic Respiration
Aerobic respiration, on the other hand, is utilized during prolonged, moderate-intensity exercises like jogging, cycling, or swimming. This process uses oxygen to generate ATP, making it more efficient for sustained energy production over extended periods. Aerobic respiration primarily engages slow-twitch muscle fibers, enhancing endurance and preventing the rapid onset of muscle fatigue.
Maximizing oxygen use, aerobic activities support endurance training and improve overall aerobic capacity. Incorporating both anaerobic and aerobic exercise training into your routine offers a well-rounded approach to fitness, benefiting muscle growth and cardiovascular health.
Nutrition and Recovery for Maximizing Muscle Gains with Cardio
Nutrition and recovery are critical components for maximizing muscle gains when incorporating cardio into your workout routine. Proper nutrition, including adequate protein and carbohydrates, is essential for muscle repair and growth. Consuming protein shortly after a workout can enhance muscle protein synthesis, aiding in muscle hypertrophy.
Carbohydrates are equally important as they help replenish glycogen levels depleted during exercise, supporting better recovery and energy levels for subsequent workouts. A balanced post-workout meal that includes both protein and carbohydrates can optimize muscle recovery and growth.
Hydration plays a vital role in recovery. Staying well-hydrated before, during, and after workouts improves performance and reduces the risk of muscle cramps and fatigue. Efficient mitochondrial function, supported by proper nutrition and hydration, is crucial for recovery and muscle growth over time.
Common Mistakes When Combining Cardio and Strength Training
Combining cardio and strength training can be highly effective, but it’s easy to make mistakes that hinder your progress. One common error is failing to prioritize recovery and rest, leading to overtraining and potential injuries. Overtraining can result in fatigue, decreased performance, and muscle loss, counteracting your fitness goals.
Another mistake is not properly sequencing your workouts. If your primary goal is to gain muscle, perform weight training before cardio to ensure maximum strength and energy for lifting weights. If your main focus is cardiovascular fitness, doing cardio first serves as an effective warm-up for your muscles.
Tips for Effectively Balancing Cardio and Resistance Training
Balancing cardio and resistance training requires strategic planning to achieve the best results. Incorporating both types of exercise can enhance overall fitness and muscle growth. High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) offers a time-efficient way to combine the benefits of cardio and strength training.
Scheduling specific days for cardio and strength training ensures optimal recovery and performance. For instance, alternating between cardio and weight training days can prevent overtraining and allow your muscles to recover adequately. Circuit training, which combines cardio and strength exercises in a single session, can also be an effective approach to keep your heart rate elevated while building muscle.
Monitoring your workout progress is crucial for continuous improvement and achieving goals. Adjusting your routine based on performance and recovery can help maintain a balanced focus on both cardio and strength training, avoiding muscle imbalances and ensuring consistent progress.

Summary
In summary, cardio exercise can indeed contribute to muscle growth when integrated effectively with resistance training. Understanding the science behind different types of cardio, such as HIIT, LISS, and HIIRT, allows you to tailor your workouts for optimal muscle hypertrophy and cardiovascular health. Concurrent training, proper nutrition, and recovery are key to maximizing the benefits of combining cardio and strength training.
By avoiding common mistakes and following strategic tips for balancing cardio and resistance training, you can achieve a well-rounded fitness routine that supports muscle gains and overall health. Embrace the power of cardio and weight training together, and watch your fitness goals become a reality.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can cardio really build muscle?
Absolutely! Incorporating high-intensity interval training (HIIT) alongside resistance training can help you build muscle while improving your cardiovascular fitness.
How should I sequence my workouts for maximum muscle gain?
For maximum muscle gain, prioritize weight training before cardio to ensure you have the energy needed for your strength workouts. This sequencing helps you lift heavier and more effectively, promoting muscle growth.
What is the role of nutrition in maximizing muscle gains with cardio?
To maximize muscle gains while doing cardio, focus on proper nutrition by ensuring you get enough protein and carbohydrates. This will support muscle repair and growth, helping you achieve better results.
Can too much cardio lead to muscle loss?
Absolutely, too much cardio can indeed lead to muscle loss if you're not pairing it with strength training and giving your body enough time to recover. It's all about finding that balance!
How can I balance cardio and resistance training effectively?
To effectively balance cardio and resistance training, try scheduling specific days for each and incorporate HIIT for maximum results. Keeping track of your progress will also ensure you're on the right path!